Diving into the world of stock options, we unravel the complexities of trading strategies and tax implications, providing a comprehensive overview that will leave you informed and ready to take on the market.
Understanding stock options
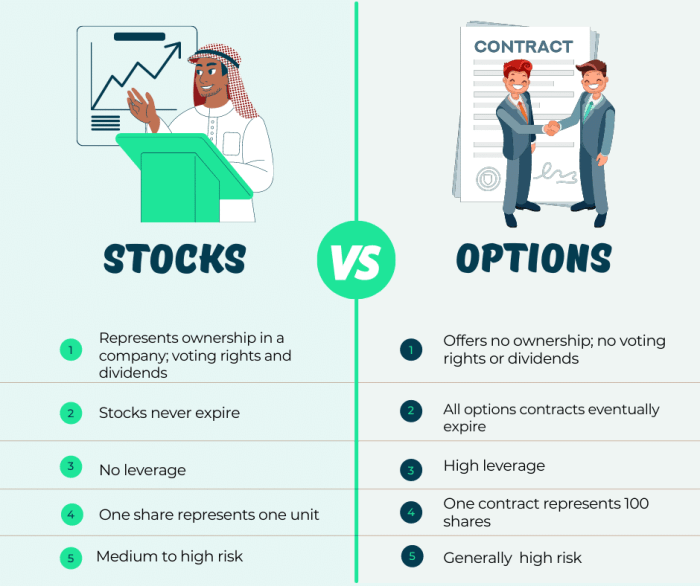
Stock options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of a particular stock at a predetermined price within a set time frame. They are commonly used for hedging, speculation, and income generation in the financial markets.
Examples of stock options in practice
- A call option gives the holder the right to buy a stock at a specified price before the expiration date. For example, if you buy a call option for Apple stock at $150 with an expiration date in three months, you can exercise the option and buy the stock at $150, even if the market price is higher.
- A put option gives the holder the right to sell a stock at a specified price before the expiration date. For instance, if you purchase a put option for Tesla stock at $700 with an expiration date in six months, you can sell the stock at $700, regardless of the market price.
Difference between call and put options
- Call options are used when investors expect the price of the underlying stock to rise, while put options are utilized when they anticipate the price to fall.
- Call options provide the opportunity to buy at a predetermined price, while put options offer the chance to sell at a specified price.
Potential benefits and risks of trading stock options
- Benefits:
- Potential for high returns with a small initial investment.
- Flexibility to profit from both rising and falling stock prices.
- Risks:
- Potential loss of the entire investment if the option expires worthless.
- Leverage can amplify losses as well as gains.
Types of stock options
When it comes to stock options, there are two main types that investors should be aware of: incentive stock options (ISOs) and non-qualified stock options (NSOs).
Incentive Stock Options (ISOs)
- ISOs are typically offered to employees as part of their compensation package.
- They have special tax advantages, as they are not subject to ordinary income tax upon exercise.
- However, in order to qualify for these tax benefits, certain conditions must be met, such as holding the stock for a specific period of time.
Non-Qualified Stock Options (NSOs)
- NSOs do not offer the same tax benefits as ISOs and are subject to ordinary income tax upon exercise.
- They are often used for consultants, advisors, or other individuals who are not employees of the company.
- While NSOs may not have the same tax advantages as ISOs, they do offer more flexibility in terms of who can receive them.
It’s important for investors to understand the differences between ISOs and NSOs in order to make informed decisions about their stock option compensation.
Factors influencing stock options
When it comes to stock options, several factors come into play that can impact their pricing. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors looking to navigate the options market effectively.
Market Volatility, Time to Expiration, and Underlying Stock Price:
Market volatility plays a significant role in determining the value of stock options. Higher volatility typically leads to increased option premiums, as there is a greater likelihood of significant price movements. Time to expiration is another crucial factor, with options losing value as they approach their expiration date. The underlying stock price also plays a key role, as the relationship between the stock price and the option strike price affects the option’s intrinsic value.
Interest Rates
Interest rates can have a direct impact on stock option pricing. Higher interest rates generally lead to higher option premiums, as investors have the opportunity to earn more by investing their money elsewhere. On the other hand, lower interest rates can result in lower option premiums, as the cost of holding options decreases.
Dividends
Dividends can also influence stock option pricing. When a company pays out dividends, the stock price typically drops by the amount of the dividend. This can have a negative impact on call options, as the potential for stock price appreciation is reduced. On the other hand, put options may benefit from dividends, as they can provide a cushion against potential price declines.
Strategies for trading stock options
When it comes to trading stock options, there are several popular strategies that investors can use to maximize their profits and manage risks effectively.
Covered Calls
Covered calls are a common strategy where an investor owns the underlying stock and sells a call option on that stock. This strategy allows the investor to generate income from the premiums received while still holding onto the stock. For example, if an investor owns 100 shares of Company XYZ, they can sell a call option with a strike price above the current market price. If the stock price remains below the strike price, the investor keeps the premium as profit.
Protective Puts
Protective puts involve buying a put option on a stock that an investor already owns. This strategy acts as insurance against a potential decline in the stock price. For instance, if an investor owns shares of Company ABC and buys a put option with a strike price below the current market price, they can protect themselves from significant losses if the stock price drops below the strike price.
Straddles
A straddle is a strategy where an investor buys both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is used when the investor expects a significant price movement in either direction but is unsure of the direction. By using a straddle, the investor can profit from the volatility of the stock price. For example, if a company is set to announce earnings, an investor can use a straddle to benefit from a potential price swing regardless of whether it goes up or down.
It is crucial to practice risk management when trading stock options to protect your investments. This includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and only investing money that you can afford to lose. By implementing these strategies and managing risks effectively, investors can navigate the stock options market with confidence and achieve their financial goals.
