Hey there, fellow students! Let’s dive into the world of student loan repayment options. From federal programs to private loan strategies, we’ve got you covered with all the deets you need to know. So, grab your latte and get ready for some serious money talk!
Now, let’s break down the nitty-gritty details of the different repayment plans available for your student loans.
Understanding Student Loan Repayment Options
When it comes to paying back those student loans, it’s essential to know your options to avoid any financial pitfalls down the road. Let’s break down the different repayment plans available and help you navigate through the process smoothly.
Types of Student Loan Repayment Plans
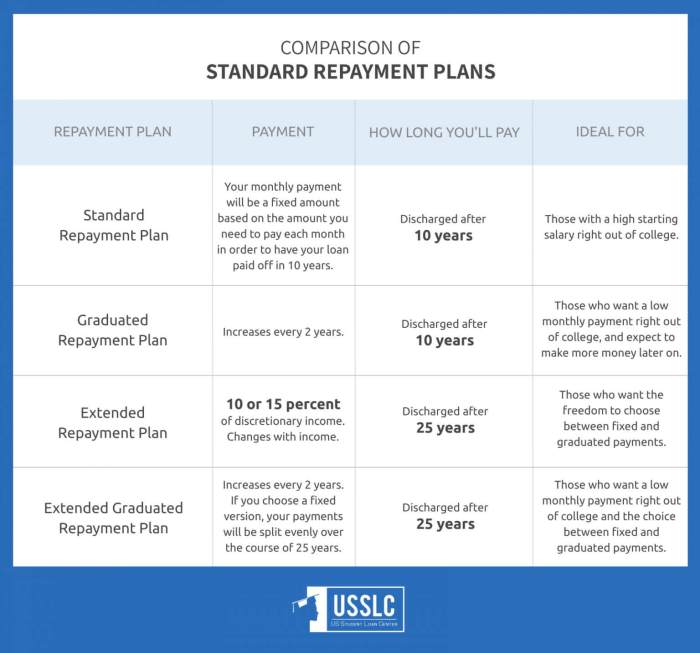
- Standard Repayment Plan: This plan involves fixed monthly payments over a period of 10 years. It’s a straightforward option for those looking to pay off their loans quickly.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Examples include Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR).
Eligibility Criteria for Each Repayment Option
- Standard Repayment Plan: Available for all federal student loan borrowers.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Eligibility criteria vary but typically require demonstrating financial need and having eligible federal student loans.
Comparison of Income-Driven vs. Standard Repayment Plans
- Income-Driven Plans offer more flexibility by adjusting payments based on your income, making it easier to manage during financial hardships.
- Standard Repayment Plans may have higher monthly payments but allow you to pay off the loan faster, saving money on interest in the long run.
Federal Student Loan Repayment Options
Federal student loans offer various repayment programs to help borrowers manage their debt effectively. These options are designed to provide flexibility based on individual financial situations.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-Driven Repayment Plans are federal student loan repayment options that base monthly payments on the borrower’s discretionary income. There are several types of income-driven plans, including Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR).
- Benefits:
- Lower monthly payments: Payments are calculated based on income, making them more manageable.
- Potential loan forgiveness: After a certain period of time (usually 20-25 years), any remaining balance may be forgiven.
- Drawbacks:
- Extended repayment period: Extending the repayment period can result in paying more interest over time.
- Tax implications: Any forgiven amount at the end of the repayment term may be considered taxable income.
Consolidating Federal Student Loans
Consolidating federal student loans involves combining multiple federal loans into a single loan with one monthly payment. This can streamline the repayment process and potentially lower monthly payments by extending the repayment term.
It’s important to note that consolidating federal student loans may result in losing certain benefits, such as interest rate discounts or loan forgiveness options.
Private Student Loan Repayment Options
When it comes to repaying private student loans, borrowers have a few options to consider. Unlike federal student loans, private loans are not eligible for income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs. However, private lenders may offer some flexibility in repayment terms.
Repayment Plans for Private Student Loans
- Standard Repayment Plan: This option involves making fixed monthly payments over a set period of time until the loan is fully repaid. The monthly payments are typically higher compared to other plans, but borrowers can save on interest in the long run.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: With this plan, the monthly payments start off lower and gradually increase over time, usually every two years. This can be beneficial for borrowers who expect their income to rise steadily in the future.
- Interest-Only Repayment Plan: Borrowers have the option to make interest-only payments for a certain period, usually up to four years. This can help reduce the initial financial burden, but it’s important to note that the principal balance will remain the same.
Interest Rates and Terms
Private student loan interest rates and terms vary depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness. Generally, interest rates for private loans tend to be higher compared to federal loans. Borrowers with excellent credit may qualify for lower interest rates, while those with poor credit may face higher rates. It’s important to carefully review the terms and conditions of the loan agreement to understand the repayment requirements.
Negotiating Repayment Terms
When negotiating repayment terms with private lenders, borrowers can explore options such as extending the repayment period, requesting lower interest rates, or modifying the repayment schedule to better align with their financial situation.
It’s important to communicate openly with the lender and provide any relevant documentation to support the request for modified terms. Keep in mind that not all lenders may be willing to negotiate, but it’s worth exploring the possibilities to make repayment more manageable.
Loan Forgiveness and Discharge Options
When it comes to student loans, there are certain conditions under which they can be forgiven or discharged, providing relief to borrowers facing financial challenges.
Loan Forgiveness Programs for Different Professions
There are various loan forgiveness programs available for individuals in specific professions, such as:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) for those working in qualifying public service jobs.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness for educators working in low-income schools.
- Loan forgiveness programs for healthcare professionals like doctors and nurses serving in underserved areas.
Implications of Loan Forgiveness on Taxes and Financial Planning
It’s important to note that loan forgiveness may have tax implications. The forgiven amount may be considered taxable income, which could impact your tax liability. Additionally, receiving loan forgiveness could affect your future financial planning, as it may impact your eligibility for certain programs or benefits.
