Yo, diving into the world of student loan interest rate calculation, get ready to crunch some numbers and understand how those interest rates really work. From fixed to variable rates, we’ve got you covered with all the deets you need to know.
Get ready to level up your knowledge on student loan interest rates with our breakdown of calculation methods, key factors, and strategies for managing those interest rates.
Understanding Student Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to student loans, understanding how interest rates work is key to managing your debt effectively. Interest rates determine how much extra you’ll pay on top of the amount you borrowed. Let’s break it down further.
Types of Student Loan Interest Rates
- Fixed Interest Rate: This type of interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan, providing predictability in monthly payments.
- Variable Interest Rate: These rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially leading to lower initial rates but higher payments later on.
- Subsidized Interest Rate: With subsidized loans, the government pays the interest while you’re in school or during deferment periods, helping to keep your balance from growing.
- Unsubsidized Interest Rate: In contrast, unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the moment the funds are disbursed, increasing the total amount you owe.
Importance of Understanding Interest Rates for Student Loans
Interest rates play a significant role in determining the total cost of your education. By understanding how interest rates are calculated and the different types available, you can make informed decisions about borrowing and repayment. It’s crucial to consider the impact of interest rates on your finances to avoid unnecessary debt and plan for a successful financial future.
Factors Affecting Student Loan Interest Rates
When it comes to student loan interest rates, several key factors come into play. These factors can greatly influence the amount of interest you end up paying over the life of your loan. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about your student loans.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the life of the loan, providing predictability and stability in monthly payments. On the other hand, variable interest rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially resulting in lower initial rates but higher rates later on. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each type of interest rate before choosing the best option for your situation.
Credit Score Impact
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the interest rate you qualify for. A higher credit score generally leads to lower interest rates, as it indicates a lower risk for the lender. On the contrary, a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates or difficulty in obtaining a loan. It’s essential to maintain a good credit score to secure better interest rates on your student loans.
Loan Term Length Influence
The length of your loan term can also impact the interest rate you receive. Shorter loan terms typically come with lower interest rates but higher monthly payments. Conversely, longer loan terms may have higher interest rates but lower monthly payments. It’s crucial to consider the trade-offs between loan term length and interest rates to find a balance that fits your financial goals and capabilities.
Calculation Methods for Student Loan Interest
When it comes to understanding student loan interest, it is crucial to grasp the calculation methods involved. By knowing how your interest is calculated, you can make more informed decisions about managing your loans and repayment strategies.
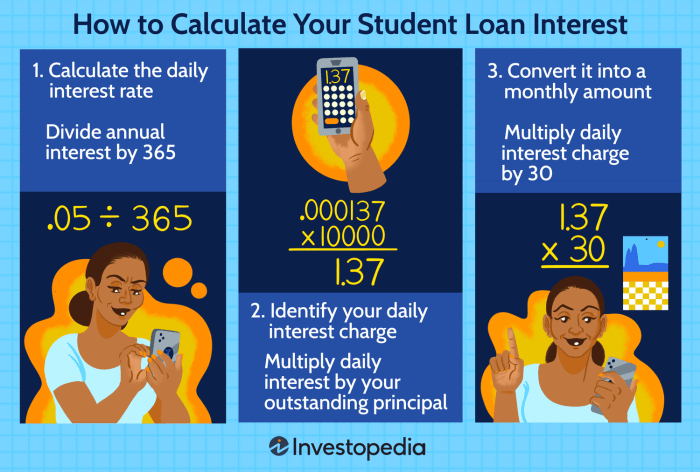
Simple Interest Formula
In most cases, student loan interest is calculated using a simple interest formula. The formula for calculating simple interest is:
Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
Where:
– Principal is the initial loan amount
– Rate is the annual interest rate (as a decimal)
– Time is the length of time the loan is outstanding (in years)
Step-by-Step Calculation
1. Determine the principal amount of your loan.
2. Identify the annual interest rate (as a decimal) on your loan.
3. Calculate the total time the loan will be outstanding in years.
4. Plug the values into the simple interest formula: Interest = Principal x Rate x Time.
5. Calculate the total amount owed by adding the interest to the principal: Total Amount = Principal + Interest.
Significance of Understanding Calculation Methods
It is important for borrowers to understand the calculation methods for student loan interest because it allows them to:
– Know exactly how much interest they will pay over the life of the loan.
– Make informed decisions about repayment strategies, such as paying extra towards the principal to reduce interest costs.
– Understand how changes in the loan amount, interest rate, or repayment term can impact the total amount owed.
– Be aware of any discrepancies in interest calculations by servicers and address them promptly.
Strategies for Managing Student Loan Interest
When it comes to managing student loan interest, there are several strategies that borrowers can use to lower their overall costs and potentially save money in the long run.
Lowering Student Loan Interest Rates
- Consider federal loan consolidation: By consolidating multiple federal loans into one new loan, borrowers may be able to secure a lower fixed interest rate, simplifying repayment.
- Explore loan forgiveness programs: Certain professions, such as teachers or public servants, may be eligible for loan forgiveness programs that can reduce or eliminate the remaining balance on their loans.
- Automatic payment discounts: Some lenders offer interest rate discounts for borrowers who sign up for automatic payments, helping to reduce the overall interest accrued on the loan.
Benefits of Refinancing Student Loans
- Lower interest rates: Refinancing allows borrowers to replace their current loans with a new loan at a lower interest rate, potentially saving money on interest payments over time.
- Consolidation of loans: Refinancing multiple loans into a single loan can simplify repayment and potentially secure a lower interest rate, making it easier to manage debt.
- Improved loan terms: Borrowers may be able to choose a new repayment term or variable interest rate, providing more flexibility in managing their loans.
Making Extra Payments to Reduce Interest Costs
- Target high-interest loans first: By focusing on paying off loans with the highest interest rates first, borrowers can reduce the overall amount of interest accrued over the life of the loan.
- Make biweekly payments: Splitting monthly payments into biweekly payments can help reduce the principal balance faster, leading to lower overall interest costs.
- Use windfalls or bonuses: Applying extra money from tax refunds, bonuses, or other windfalls directly to the loan principal can help shorten the repayment period and reduce interest costs.
