With debt-to-income ratio explained at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling American high school hip style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Debt-to-income ratio is like a secret code in the financial world, revealing how much of your income goes towards paying off debts. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty details of this crucial financial metric.
What is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
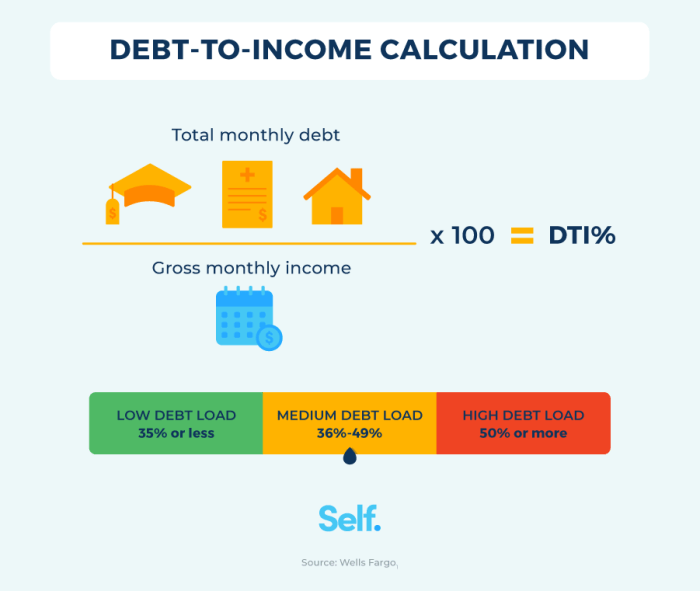
Debt-to-Income Ratio is a financial metric that compares the amount of debt you owe to your overall income.
It is calculated by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
How Debt-to-Income Ratio is Calculated
- Start by adding up all your monthly debt payments, including mortgage, car loans, credit card payments, and student loans.
- Next, calculate your gross monthly income, which is your total income before taxes and deductions.
- Divide your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income.
- Multiply the result by 100 to get your debt-to-income ratio percentage.
Examples of How Debt-to-Income Ratio Affects Financial Health
- A high debt-to-income ratio (above 43%) indicates that you may have difficulty managing your debt and may struggle to make payments on time.
- Lenders often use debt-to-income ratio to determine your creditworthiness and ability to repay a loan.
- Having a low debt-to-income ratio (below 36%) shows that you have a healthier financial situation and may qualify for better loan terms and interest rates.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio
Maintaining a healthy debt-to-income ratio is crucial for financial well-being and stability. This ratio is a key factor that lenders consider when evaluating an individual’s creditworthiness and ability to manage additional debt.
Why Debt-to-Income Ratio is Important for Lenders
- Lenders use the debt-to-income ratio to assess a borrower’s ability to repay a loan.
- A lower ratio indicates that a borrower has more disposable income available to meet monthly debt obligations.
- High debt-to-income ratios may signal financial strain and increase the risk of default, making lenders hesitant to approve new credit.
- By analyzing this ratio, lenders can make informed decisions on loan approvals and set appropriate interest rates.
How Debt-to-Income Ratio Impacts Borrowing Capacity
- A higher debt-to-income ratio limits a borrower’s ability to take on additional debt, such as a mortgage or car loan.
- Lenders may offer lower loan amounts or less favorable terms to individuals with high ratios to mitigate the risk of default.
- On the other hand, a lower debt-to-income ratio increases borrowing capacity, allowing individuals to qualify for larger loans with better terms.
Benefits of a Low Debt-to-Income Ratio
- Having a low debt-to-income ratio can lead to lower interest rates on loans, saving money in the long run.
- It provides financial flexibility and enables individuals to pursue major life goals, such as buying a home or starting a business.
- Individuals with low ratios are better positioned to weather financial emergencies or unexpected expenses without falling into excessive debt.
Understanding Good vs. Bad Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-income ratio is a crucial metric that helps determine your financial health. It is essential to differentiate between a good and a bad debt-to-income ratio to make informed decisions about your finances.
A good debt-to-income ratio is typically below 36%. This means that your total monthly debt payments should not exceed 36% of your gross monthly income. On the other hand, a bad debt-to-income ratio is anything above this threshold. Having a high debt-to-income ratio can have serious consequences on your financial stability.
Consequences of a High Debt-to-Income Ratio
Having a high debt-to-income ratio can lead to various negative outcomes, including:
- Difficulty in obtaining new credit: Lenders may be hesitant to extend new credit to individuals with high debt-to-income ratios, as it indicates a higher risk of default.
- Higher interest rates: Even if you are approved for credit, you may end up paying higher interest rates due to your high debt levels.
- Strain on your budget: A high debt-to-income ratio means a significant portion of your income goes towards debt payments, leaving you with less money for essential expenses or savings.
- Impact on credit score: A high debt-to-income ratio can negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to qualify for favorable loan terms in the future.
- Risk of default: Ultimately, a high debt-to-income ratio increases the risk of defaulting on your debts, which can have long-lasting consequences on your financial well-being.
Factors Influencing Debt-to-Income Ratio
When calculating your debt-to-income ratio, there are several factors that can significantly impact the final number. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing your financial health effectively.
Income Level
Your income level plays a major role in determining your debt-to-income ratio. A higher income means you have more financial resources to cover your debts, resulting in a lower ratio. On the other hand, a lower income may lead to a higher ratio, indicating that you are more financially strained.
Debt Levels
The amount of debt you owe directly affects your debt-to-income ratio. The more debt you have, the higher your ratio will be. Paying off debt can lower your ratio, while taking on more debt will increase it. It’s essential to balance your debt levels with your income to maintain a healthy ratio.
Types of Debt
Different types of debt can impact your ratio differently. For example, mortgage debt is considered more favorable than high-interest credit card debt. This is because mortgage debt is typically an investment in a property, while credit card debt is often associated with consumer spending. Understanding the types of debt you have can help you prioritize repayments and manage your ratio effectively.
Credit Score
Your credit score also plays a crucial role in determining your debt-to-income ratio. A higher credit score can make it easier for you to access lower interest rates and better loan terms, which can positively impact your ratio. On the other hand, a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates and unfavorable loan terms, leading to a higher ratio.
Changes in Financial Situation
Any changes in your income or debt levels can directly influence your debt-to-income ratio. For example, getting a raise at work may lower your ratio, while taking out a large loan can increase it. It’s important to regularly reassess your financial situation and adjust your debt repayments accordingly to maintain a healthy ratio.
Strategies to Improve Debt-to-Income Ratio
To improve your debt-to-income ratio, you need to focus on lowering your debt and increasing your income. This will help you achieve a healthier financial standing and qualify for better loan terms.
Reduce Debt
- Create a budget and stick to it to prioritize paying off high-interest debt first.
- Consider snowball or avalanche methods to pay off debt faster.
- Avoid taking on new debt while working on paying off existing debt.
Increase Income
- Look for ways to increase your income, such as taking on a side hustle or asking for a raise at work.
- Consider selling items you no longer need or use to generate extra cash.
- Invest in your skills or education to advance in your career and earn more.
Debt Consolidation or Refinancing
Debt consolidation or refinancing can help you combine multiple debts into one loan with a lower interest rate, making it easier to manage and pay off.
- Explore debt consolidation loans or balance transfer credit cards to simplify your debt repayment process.
- Refinance high-interest loans or mortgages to secure a lower interest rate and reduce monthly payments.
- Consult with a financial advisor to determine the best approach for your specific financial situation.
