Yo, peeps! Ready to dive into the world of budgeting like a boss? In this lit passage, we’ll break down the key deets on how to budget, helping you level up your financial game. So grab your snacks and let’s get started!
Budgeting is not just about numbers; it’s a lifestyle that can totally transform how you handle your moolah. From setting dope financial goals to crafting a budget plan that fits like your fave pair of kicks, we’ve got your back every step of the way.
Importance of Budgeting
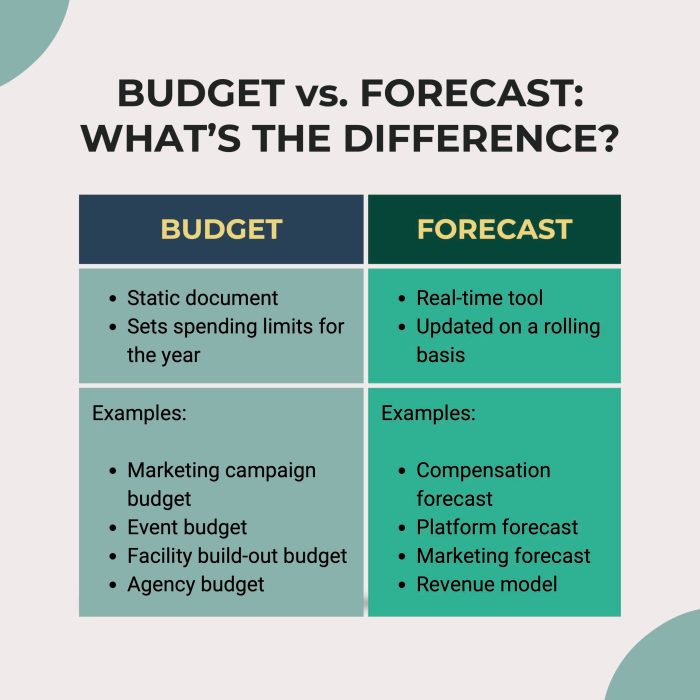
Budgeting is a crucial aspect of personal finance that can have a significant impact on one’s financial well-being. By creating a budget, individuals can track their income and expenses, allocate funds to different categories, and ultimately take control of their financial situation.
Financial Goals Achievement
Budgeting plays a key role in helping individuals achieve their financial goals. By setting specific targets such as saving for a vacation, buying a new car, or building an emergency fund, budgeting allows individuals to allocate funds accordingly and track their progress towards these goals. Without a budget, it can be challenging to save consistently and work towards achieving long-term financial objectives.
Improving Financial Discipline
Budgeting also helps improve financial discipline by creating awareness of spending habits and identifying areas where expenses can be reduced. By tracking expenses regularly and sticking to a predetermined budget, individuals can avoid overspending, prioritize essential expenses, and make informed financial decisions. Additionally, budgeting can help individuals build healthy financial habits by promoting mindful spending and saving practices.
Setting Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is a crucial step in the budgeting process. It involves identifying what you want to achieve with your money in the short-term and long-term. By setting clear financial goals, you give yourself direction and motivation to stick to your budget and make informed financial decisions.
Short-Term and Long-Term Financial Goals
- Short-term financial goals are typically achievable within a year or less. Examples include building an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, or saving for a vacation.
- Long-term financial goals, on the other hand, are objectives that may take several years to accomplish. These can include buying a home, saving for retirement, or funding a child’s education.
Aligning Budgeting with Financial Goals
Budgeting plays a crucial role in helping you achieve your financial goals. By creating a budget that prioritizes your goals, you can allocate your income towards what matters most to you. This alignment ensures that you are actively working towards your objectives and not getting sidetracked by unnecessary expenses.
Common Financial Goals
- Building an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Paying off high-interest debt to improve financial health.
- Saving for a major purchase like a car or home.
- Investing for retirement to secure future financial stability.
- Setting aside money for travel or other personal goals.
Creating a Budget Plan
Budgeting is crucial for managing your finances effectively. It helps you stay on track with your spending, save for the future, and achieve your financial goals. Here are the steps involved in creating a budget plan:
Step 1: Calculate Your Income
- List down all your sources of income, including salary, bonuses, and any other earnings.
Step 2: Identify Your Expenses
- Track your expenses for a month to understand where your money is going.
- Categorize your expenses into fixed (rent, utilities) and variable (dining out, entertainment).
Step 3: Set Financial Goals
- Determine your short-term and long-term financial goals, such as saving for a vacation or retirement.
- Allocate a portion of your income towards achieving these goals.
Choosing a Budgeting Method
- Zero-Based Budgeting: Assign every dollar of your income to a specific expense or savings category.
- 50/30/20 Rule: Allocate 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment.
Tracking Expenses Effectively
- Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to monitor your spending and stay within your budget limits.
- Review your budget regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure you are meeting your financial goals.
Managing Income and Expenses
Effective budgeting involves not only setting financial goals and creating a plan but also managing income and expenses wisely. By strategically handling both aspects, individuals can stay on track with their budget and work towards achieving their financial objectives.
Strategies for Managing Income
- Track your income sources: Keep a record of all your income streams, including salaries, bonuses, freelance work, or any other sources of revenue.
- Create a budget based on your income: Allocate a specific percentage of your income to different expense categories, such as housing, groceries, utilities, and savings.
- Consider multiple income streams: Explore opportunities for additional income through side hustles or investments to boost your overall financial stability.
Reducing Expenses and Cutting Costs
- Identify unnecessary expenses: Review your spending habits to identify areas where you can cut back, such as dining out, subscription services, or impulse purchases.
- Comparison shop for essentials: Look for deals and discounts when purchasing necessities like groceries, insurance, or utilities to save money.
- Set spending limits: Establish limits for discretionary spending categories to avoid overspending and stay within your budget constraints.
Prioritizing Expenses to Align with Financial Goals
- Focus on essentials first: Ensure that critical expenses like housing, utilities, and debt payments are covered before allocating funds to non-essential items.
- Allocate funds to savings and investments: Prioritize saving for emergencies, retirement, or other financial goals by setting aside a portion of your income regularly.
- Adjust spending based on goals: Monitor your progress towards financial objectives and make adjustments to your budget as needed to stay on course.
Emergency Fund and Savings
Having an emergency fund is crucial for financial stability. It acts as a safety net in unexpected situations like medical emergencies, job loss, or major repairs. Without an emergency fund, individuals may resort to taking on debt to cover these unforeseen expenses.
Allocating Savings in a Budget
When creating a budget, it’s important to prioritize savings. A general rule of thumb is to allocate at least 20% of your income towards savings. This can include saving for retirement, emergencies, or specific goals like buying a house or going on a vacation.
- Set specific savings goals to stay motivated and track your progress.
- Automate your savings by setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account.
- Consider opening a high-yield savings account to earn more interest on your savings.
Role of Savings in Financial Stability
Savings play a vital role in achieving financial stability and security. They provide a cushion during tough times and help you avoid falling into debt. Additionally, having savings can give you peace of mind and the flexibility to pursue opportunities that require upfront costs.
Remember, it’s never too late to start saving. Every little bit counts towards building a secure financial future.
Reviewing and Adjusting Budget
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your budget is crucial to ensure that you are on track with your financial goals and adapting to any changes in your income or expenses.
Importance of Reviewing a Budget Regularly
Reviewing your budget regularly allows you to track your spending habits, identify any areas where you may be overspending, and make necessary adjustments to stay within your financial limits.
Identifying Areas for Adjustment in a Budget
- Compare your actual expenses to your budgeted amounts to see where you may be overspending.
- Look for recurring expenses that can be reduced or eliminated to free up more funds for savings or other financial goals.
- Identify any unexpected expenses that may have come up and adjust your budget accordingly.
Adapting a Budget to Changing Financial Circumstances
- Update your budget whenever there are changes in your income, such as a raise or a decrease in salary.
- Adjust your budget if you encounter unexpected expenses or if your financial goals change.
- Consider reallocating funds from one category to another to accommodate new priorities or changes in expenses.
